What if modern eukaryotes made modern protosterols? A paleontologist’s guide to the discovery of modern intermediates
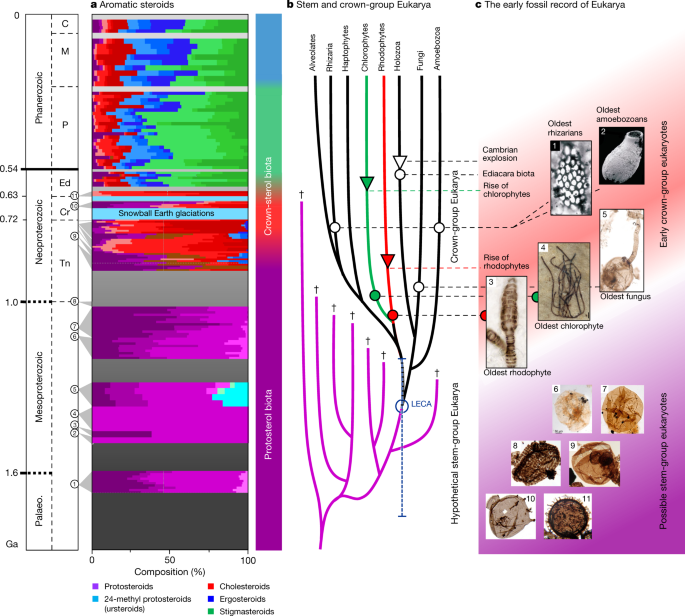
The team combed rocks from around the world and found widespread traces of these ‘protosterols’ — evidence that the eukaryotes that produced them were abundant in water environments between 800 million and 1.6 billion years ago.
Most modern eukaryotes rely on fat-like compounds called sterols, such as cholesterol, to build cell membranes and carry out other cellular functions. Because sterols are found throughout the eukaryotic family tree, they are thought to have been present in the last common ancestor of all modern eukaryotes. The compounds are being used by the palaeontologists to get an idea of the presence of eukaryotes.
But Andrew Roger, who studies comparative genomics and the evolution of eukaryotes at Dalhousie University in Halifax, Canada, notes that fossilized red and green algae dating back one billion years look remarkably similar to living algae, and probably made modern sterols. That would suggest that modern sterols — not just their precursors — should also be present in rocks that are more than 800 million years old. “The finding raises as many questions as it answers,” he says.
There is a chance that researchers are looking for the wrong molecule. Benjamin Nettersheim, a geobiologist at the University of Bremen in Germany, Jochen Brocks, a palaeobiogeochemist at the Australian National University in Canberra, and their colleagues decided to focus on short-lived molecules that modern eukaryotes make while synthesizing sterols. The end product might have been the modern intermediates.
But the team’s approach — using hypotheses about the evolution of biosynthetic pathways to guide the search for ancient life — could reveal more about early life, she adds. “It’s thinking about the record of biomarkers from an evolutionary perspective,” Porter says. I think that is necessary.
While there are reasons to suspect that the Protosterols were made by humans, the researchers have not been able to determine if they were made by ancientbacteria, as a possibility, according to Susannah Porter, a paleontologist.
Beghin, J. et al. Microfossils from the late Mesoproterozoic–early Neoproterozoic Atar/El Mreïti Group, Taoudeni Basin, Mauritania, northwestern Africa. Precambrian Res. 291, 63–82 (2017).
Organization of micro-ablation techniques for the removal of drilling fluids and other contaminants from marine fragmented and fissile rock material
Jarrett, A., Schinteie, R., Hope, J. M. & Brocks, J. J. Micro-ablation, a new technique to remove drilling fluids and other contaminants from fragmented and fissile rock material. There are people in the organization. Geochem. 61, 57–65 (2013).
Variations in the sterane carbon number distributions of marine source rock derived crude oils through geological time. The name of the organization. Geochem. 12, 61–73 (1988).
Schinteie, R. The impact of drill coreContamination on compound-specific carbon and hydrogen signatures. There is an official organization. Geochem. 128, 161–171 (2019).
Zumberge, J. A., Rocher, D. & Love, G. D. Free and kerogen-bound biomarkers from late Tonian sedimentary rocks record abundant eukaryotes in mid-Neoproterozoic marine communities. Geobiology 18, 326–347 (2019).
Brocks, J. J., Grosjean, E. & Logan, G. A. Assessing biomarker syngeneity using branched alkanes with quaternary carbon (BAQCs) and other plastic contaminants. Someone named Geochim. Cosmochim. The work was titled, “Acta 72, 871–888.”
Brocks, J. J. & Hope, J. M. Tailing of chromatographic peaks in GC–MS caused by interaction of halogenated solvents with the ion source. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 52, 471–475 (2014).
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06170-w
Energy metabolism in terrestrial eukaryotic anaerobes: the origin of the Sturtian Snowball Earth. Vol. 34, 441-469 (2003)
Holba, A. G. There are indicators of input from fresh water environments. They are called the organization of the domain of geography. 34, 441–469 (2003).
Mentel, M. & Martin, W. Energy metabolism among eukaryotic anaerobes in light of Proterozoic ocean chemistry. There is a man named Phil. R.S. B 363 was released in 2008.
Brocks, J. J. Early sponges and toxic protists may have been the progenitors of the Sturtian Snowball Earth. The journal of geology 14, 129–149 is published.
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06170-w
Oxygen and sterols in aerobic life: a new class of organisms that influence the survival of plasma membrane behavior and yeast survival in dehydration
Special relation between oxygen and sterols in aerobic life. There is free radical. Med. 47, 880 (2009).
Dupont, S., Beney, L., Ferreira, T. & Gervais, P. Nature of sterols affects plasma membrane behavior and yeast survival during dehydration. A new type of medicine called Biochim. There is a group of organisms called biophys. The article “Ada 1808, 1425–1528” was published in 2011.
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06170-w
On the relative age of Euphysidal Eukaryotes: Evidence from fossils, clocks, and clathrin-mediated endocytosis
M. W., Brown, and Roger are related to Eme. Evidence from fossils and clocks are used to evaluate the age of Eukaryotes. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Something else: Biol. 6, a016139 (2014).
Anderson, R. H. et al. Sterols lower energetic barriers of membrane bending and fission necessary for efficient clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Cell Rep. 37, 110008 (2021).
Zhang, X., Paoletti, M., Izon, G., Fournier, G. & Summons, R. Isotopic evidence of photoheterotrophy in Palaeoproterozoic Chlorobi. There is a preprint at Research Square. There are more than 20 years left.
Summons, R. E. et al. Distinctive hydrocarbon biomarkers from fossiliferous sediments of the Late Proterozoic Walcott Member, Chuar Group, Grand Canyon, Arizona. There is a person who is named “geochim.” Cosmochim. Acta 52, 2625–2637 (1988).
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06170-w
Evolution of Bacteria and its Impact on Eukaryogenesis. The Chuar Group, Grand Canyon (Gauge of Gangiomorpha pubescens)
Evolution of bacterium and its impact on eukaryogenesis. Proc. The Natl Acad. is a state of the art in scientific research. Sci. USA 118, e2101276118 (2021).
Butterfield, N.J., and Brocks, J. J. studied the effect of Microbiological mats on biomarker preservation. Geology 41, 103–106 (2013).
The Chuar Group, Grand Canyon contains vase-shaped microfossils which are believed to be evidence of amoebae. A monograph on Paleobiology, published in 2000.
Butterfield, N. J.Bangiomorpha pubescens n. sp. implications for the evolution of sex, multicellularity, and the Mesoproterozoic/Neoproterozoic radiation of eukaryotes. The Paleobiology 26, 386–504, was published in 2000.
N. Gueneli and her husband are present in the movie Gueneli, N. There are 1.1 billion year-old porphyrins in the marine environment. Proc. There is a Natl Acad. Sci. USA 115, E6978–E6986 (2018).