-
Why are the proposed budget cuts so large?

US President Donald Trump is proposing to cut NASA’s budget by over 50% and cut funding for the Large Hadron Collider by 40%, a study by Nature has revealed. Trump’s proposed budget also includes a 40% reduction for the LaserInterferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory, which has sites in Louisiana and Washington State. ExoMars will get zero US…
-
I have brought the voices of local fishers into ocean policies

A study of small-scale fishing practices in Senegal by a research project titled ‘Hidden Harvests’, led by Nature, found that the country’s fishers voluntarily closed certain fisheries to preserve species. In Senegal, fishers innianing immersing clay and shell pots in the sea in order to help aquatic creatures reproduce during the year added value to…
-
A citation penalty should not be given to researchers who transition into new fields

A study published in Nature reported researchers in disciplines including ecology and artificial intelligence were ‘pivoting’ away from their primary fields to research COVID-19. The study analysed 1.7 million patents granted in the United States from 1980 to 2015. Researchers found a similar phenomenon when evaluating technology areas listed in patents’ citations.
-
The golden oldies are the research papers of the last few decades

Microsoft’s ‘ImageNet’ was the top-cited paper of all time from 1955-2014, as per an analysis by Nature. It is followed by a 2009 paper ‘ImageNet: A Large-Scale hierarchicalimage database’ which is ranked number 24. Some of the most famous papers did not cite the original work because it was too expensive when it was published.
-
Many federal health workers are losing their jobs
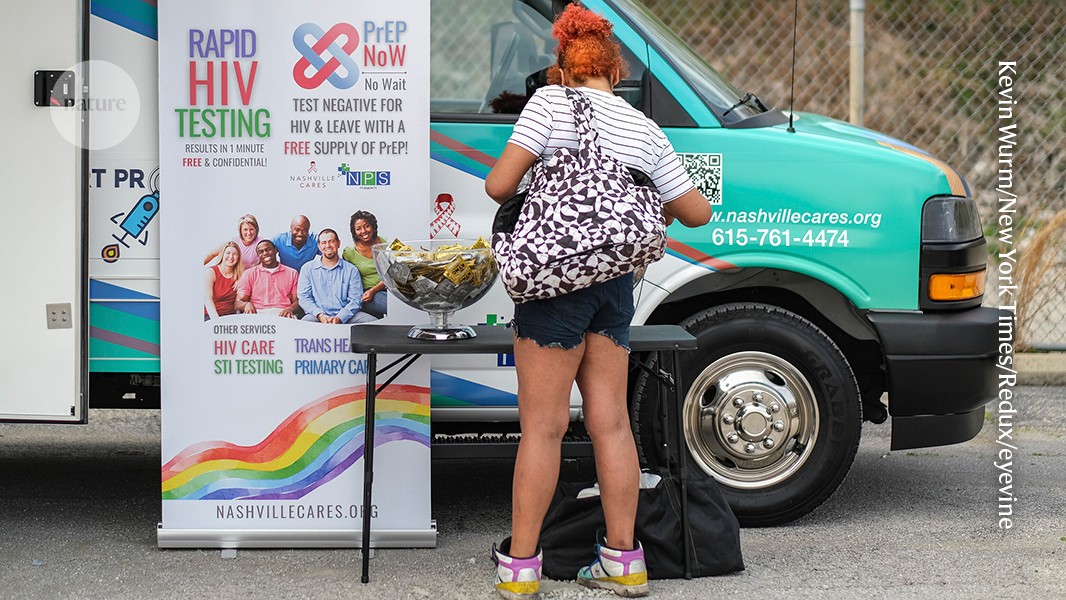
The US National Institute for Health recently cancelled over a hundred research grants funding HIV and AIDS research in the past few weeks, according to a Nature analysis. The CDC is losing its HIV prevention office as part of the restructuring. The Department of Health and Human Services, including the Centers for Disease Control and…
-
There have been a lot of firings at federal health agencies
The US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) has fired over 100 executives at the National Institutes of Health (NIH), according to Nature. The firings include several NIH directors as well as executives at the Food and Drug Administration. “These reductions in the workforce will have a profound impact on key NIH administrative functions…[and]…will…
-
What science photos can using Artificial Intelligence?

In a study published in Nature, researchers claimed that women in low-income countries are four times more likely to die from breast cancer than those in high-income countries on the basis of the most-recent available data from 2022. The study also stated that people in low-income countries are three times more likely to die due…
-
Retracts data can be used to clean up science

Jining First People’s Hospital in China is the World’s Most-Retracted Institution, a report by Nature revealed. The report used figures supplied by three private research-integrity and analytics firms. The institutions with large numbers of papers tend to have lower retraction rates. They encourage researchers to publish more articles and accrue more citations; higher counts can…
-
The next frontier in medicine is heritable polygenic editing
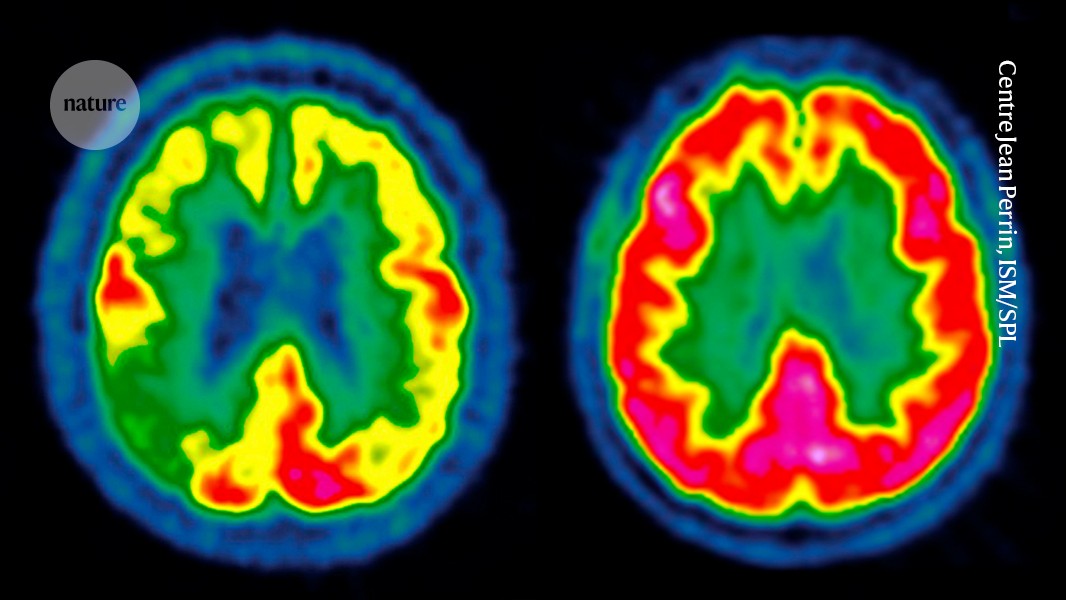
A study published in Nature has found that polygenic genome-editing technology could reduce the risk of diseases in embryos. It found that the risk of diseases in embryos could be reduced if Polygenic Genome Editing was used. It said that it is important to start a conversation about what could happen if more-sophisticated gene-editing technologies…
-
This molecule is key in slowing down the aging process
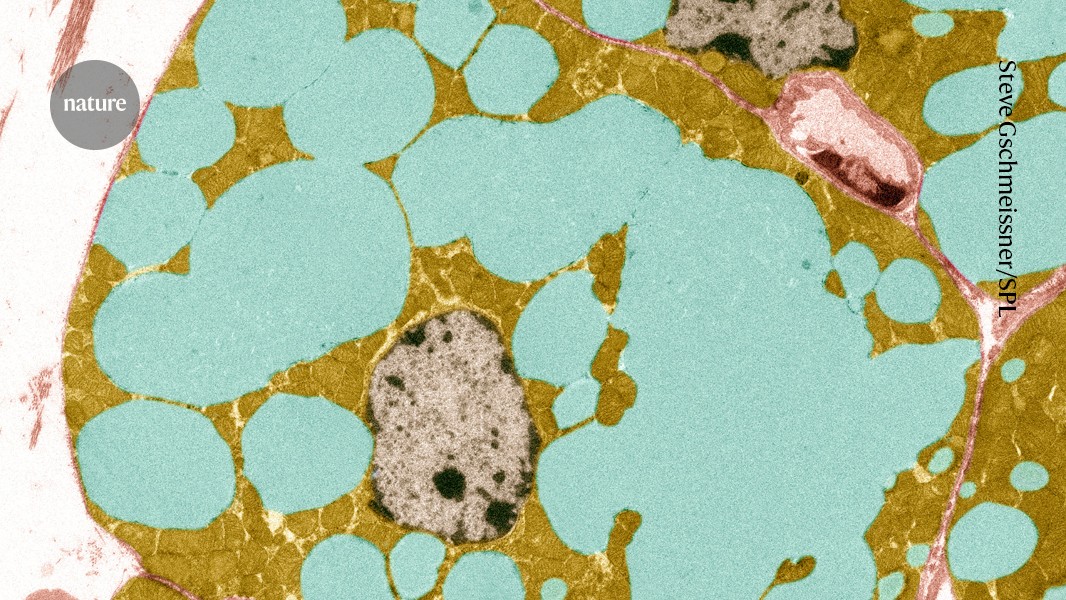
A study in Nature has found that a component of bile, lithocholic acid (LCA), triggers many of the age-defying and potentially lifespan-extending health benefits of low-calorie diets. LCA was found to extend lifespans of nematodes, fruit flies and mice when fed with lithocholic acid. The study also showed that 2 a day of added LCA…
-
Why Asia is leading in green materials

South Korea has ranked fifth in the field of materials science every year from 2019 to 2023, according to Nature’s ‘Nature Index’. Its proportion of materials science Share relative to its overall Nature Index output (49.7%), a figure higher than China (45.7%) and more than three times higher than that of the United States (15.4%).
-
The world could solve a lot of its biggest problems using science

About 6,000 people around the world were surveyed for Nature’s survey on science advice. They were asked about the quality of routine science advice to governments and about advice during a crisis like the COVID-19 pandemic. Over 60% of respondents said that science advice fails to incorporate a diversity of people or viewpoints.
-
Governments don’t use science to solve their biggest problems
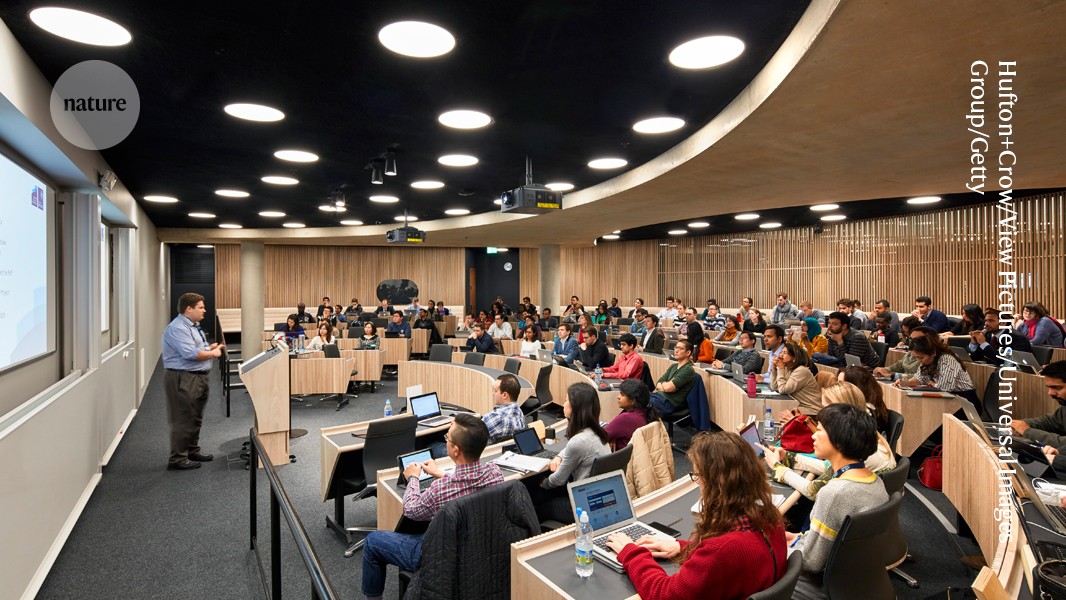

A recent survey has found that over 60% of survey respondents said science advice fails to incorporate a diversity of people or viewpoints. Science advice needs to incorporate more expertise in the future, according to the survey by the International Network for Governmental Science Advice. The survey was conducted on behalf of Nature by two…
-
The survival of the nice may be the opposite of evolution

The complexity of self-replication in the natural world is the best talk about the complex of cooperative behaviour in the natural world. It uses examples from nature to emphasise that cooperation is very common in nature. This allows each cell to adjust its gene expression in a way that benefits the individuals in the group,…
-
There is a spotlight on the disparity in global health research

The US has been the most prolific contributor of research in the Nature Index, covering all but seven of the journals tracked by the Nature Index in the subject. “It comes tops for share in all but seven of the journals tracked by the Nature Index. This includes large general journals such as Nature Communications…
-
The discovery of the lost tails took 2.5 years to publish
A study in the journal Nature by scientists at Kiel University and New York University claims to have identified the genes responsible for the short tail of a mouse. The mice had been suffering from a tailbone injury. Scientists used genetic analysis to find similarities between changes in the genomes of mice and humans. The…
-
It would be foolish to end the US–China science pact

Researchers from China, the US and Europe work together to understand the role of nature in human prosperity. Researchers from China, the US and Europe work together to understand the role of nature in human prosperity. Both Kerry and Zhenhua are moving on to new roles. Researchers from China, the US and Europe work together…
-
The artificial intelligence system was a good thing and a bad thing

A new study claims that a new type of AI called ChatGPT, developed at the Harvard Medical School, was capable of analysing more than 50,000 samples of wine in its first week. ChatGPT has the ability to analyse wine molecules in real-world conditions, as well as to detect changes in molecules as they move through…
-
The paper on room-temperature superconductivity is a big deal

The authors of ‘Hydroconductivity under Extreme Pressure’, Ranga Dias and Ashkan Salamat, have withdrawn their study from Nature magazine over alleged plagiarism. Dias was accused of plagiarizing part of his PhD thesis. Salamat was accused of plagiarising part of his PhD thesis. In March, Dias and Salamat’s paper was published in Nature but later retracted…
-
Postdocs want to get better pay and working conditions

A new survey of postdoctoral researchers, conducted by Nature, found that half the postdocs surveyed in Africa earn less than US$15k a year. The survey also revealed that more than half of postdocs said they had considered leaving their scientific field because of mental-health concerns. Over 700 postdoctoral researchers were surveyed by Nature between 2017…
-
A Turing test for artificial intelligence

An e-mail sent by a researcher to Nature about a paper on manganese disulfide’s electrical properties in January 2018 had raised concerns about possible data fabrication. It was the first time Dias had sent an e-mail to Nature since the 2022 retraction of his research. A report by four independent referees found no evidence of…
-
Racist roots in science must be acknowledged by institutions

A case study of black people in London’s chemistry department has revealed how they’re treated by the faculty. The case study, published in the journal ‘Nature’, revealed how some people are asked to leave the department after showing “disparaging” views of black people. This comes after a woman was arrested for racist comments on a…
-
What do you think about the Earth’s core changing?
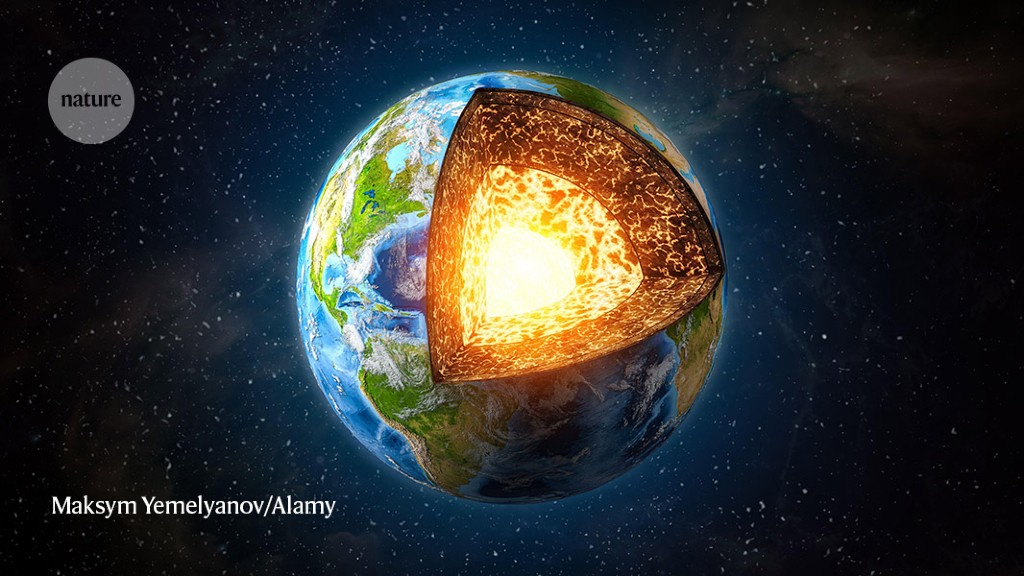

A study published in the journal Nature has revealed that waves from earthquakes pass through Earth’s innermost core, which is estimated to be around 650 km thick, differently than through the outer part. The researchers said the waves passing through the innermost part slowed down in one direction, whereas waves passing through the outer layer…
-
Is the world able to save a million species from extinction?

African countries, which are home to some of the world’s most biodiverse areas, thought that China presidency was strong-armed and would allow a deal to go through, Nature reported. The negotiating process was not equitable towards developing countries and the deal will not enable significant progress towards stemming biodiversity loss, the report said quoting a…
